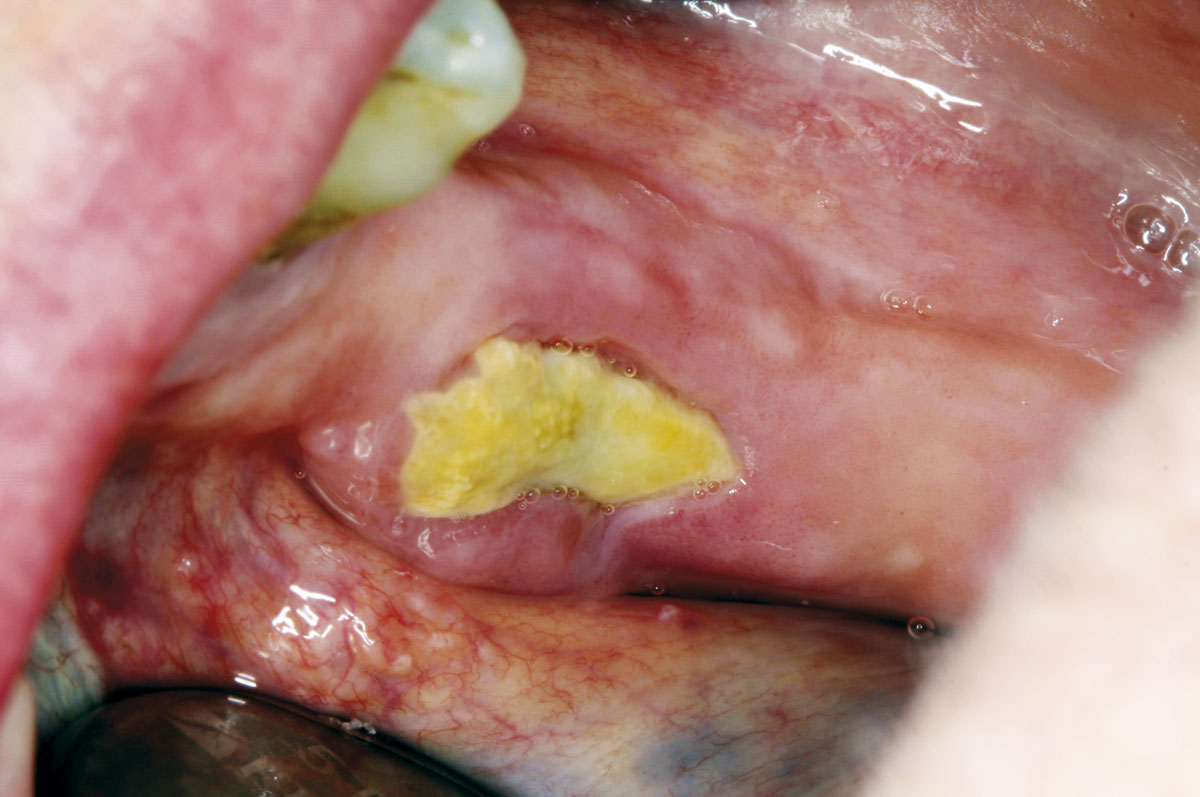
 <leadpara>Patients commencing therapy on certain classes of medications should be counselled regarding the risk of medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw (MRONJ). This is also known as anti-resorptive drug-related osteonecrosis of the jaw (ARONJ) and bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaw (BRONJ) when associated with those medications.
<leadpara>Patients commencing therapy on certain classes of medications should be counselled regarding the risk of medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw (MRONJ). This is also known as anti-resorptive drug-related osteonecrosis of the jaw (ARONJ) and bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaw (BRONJ) when associated with those medications.

MRONJ is a condition occurring in a patient who has received a bone-modifying agent (BMA) or an angiogenic inhibitor agent, with no history of head and neck radiation, where bone can be detected through an intraoral or extraoral fistula/e in the maxillofacial region that does not heal within eight weeks.
In the past two decades, there has been a steady increase in its incidence. MRONJ occurs in about 1-9% of patients with advanced cancer who are receiving a BMA, in contrast to a much smaller percentage of patients who receive BMA pharmacotherapy for osteoporosis.
While it is well-recognised that bisphosphonates and RANKL inhibitor denosumab are implicated, several drugs carry the risk of this debilitating adverse effect. These include anti-angiogenic agents, monoclonal antibodies, tyrosine kinase inhibitors and variant fusion proteins, radiopharmaceutical Radium 233, methotrexate, prednisolone and selective estrogen receptor modulator Raloxifene.
The risk appears to be higher when used in conjunction with bone-modulating therapies.
A position paper of the American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons describes a clinical staging process. MRONJ can be challenging to treat and can cause significant pain and reduced quality of life. Treatment depends on the stage of disease and the patient’s underlying medical history.
With bisphosphonates, a drug holiday is often not useful due to the incorporation of the drug into bone tissue. In contrast, many newer medications have a shorter half-life, and a drug holiday may be considered.
Management is often multidisciplinary. Treatment, according to the stage of the disease, may include conservative measures such as antimicrobial mouth rinses, antibiotics if clinically indicated, effective oral hygiene, and conservative surgical interventions, such as small sequestrum removal.
More aggressive surgical intervention may be indicated for more severe cases. Possible adjunctive therapies include hyperbaric oxygen therapy, platelet rich plasma, bone morphogenic protein, and parathyroid hormone.
Preventive oral care methods combined with effective oral health practices are associated with a lower rate of MRONJ. It is strongly recommended that patients see a dentist prior to therapy to ensure that any teeth of questionable prognosis are assessed and extracted if necessary, with adequate healing time.
Any dental prosthesis should be well fitting in order to reduce trauma. Dental screening, prophylaxis, oral hygiene instruction, tobacco and alcohol cessation counselling, and timely treatment is recommended to reduce MRONJ risk.
Key messages
- Medication-related osteonecrosis is related to various drugs, aside from bisphosphonates and denosumab
- Consequences may be debilitating.
- Dental screening and effective oral health care are important.
References available on request.
Questions? Contact the editor.
Author competing interests: nil relevant disclosures.
Disclaimer: Please note, this website is not a substitute for independent professional advice. Nothing contained in this website is intended to be used as medical advice and it is not intended to be used to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any disease, nor should it be used for therapeutic purposes or as a substitute for your own health professional’s advice. Opinions expressed at this website do not necessarily reflect those of Medical Forum magazine. Medical Forum makes no warranties about any of the content of this website, nor any representations or undertakings about any content of any other website referred to, or accessible, through this website.

